一:Mybatis连接池与实务深入
1.Mybatis连接池的分类 连接池作为可以减少我们获取连接所消耗的时间的技术。自己的连接池技术 ,通过主配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml中的dataSource标签 ,type属性 就是表示采用何种连接池方式。
<!-- 配置数据源(连接池)--> <dataSource type="POOLED" > <!-- 配置连接数据库的四个基本信息--> <property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}" /> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" /> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" /> </dataSource>
type属性的取值:
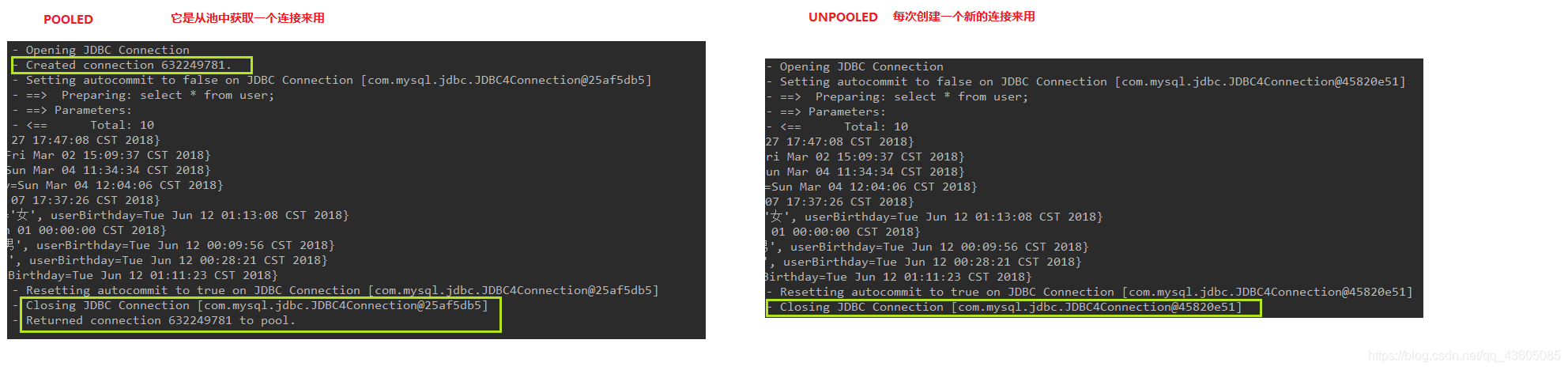
POOLED 采用传统的javax.sql.DataSource规范中的连接池 ,mybatis中有针对规范的实现传统的获取连接的方式 ,虽然也实现Javax.sql.DataSource接口,但是并没有使用池的思想 。务器提供的JNDI技术实现 ,来获取DataSource对象,不同的服务器所能拿到DataSource是不一样。
注意:如果不是web或者maven的war工程,是不能使用的。我们课程中使用的是tomcat服务器,采用连接池就是dbcp连接池。** 一般我们采用POOLED的方式**,很多时候我们所说的数据源就是为了更好的管理数据库连接,也就是我们所说的连接池技术。
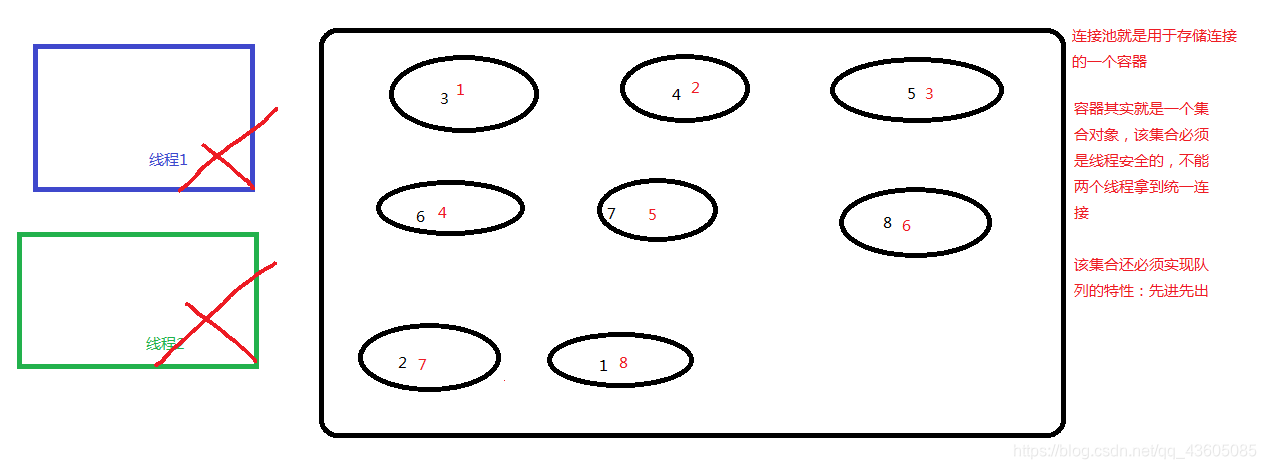
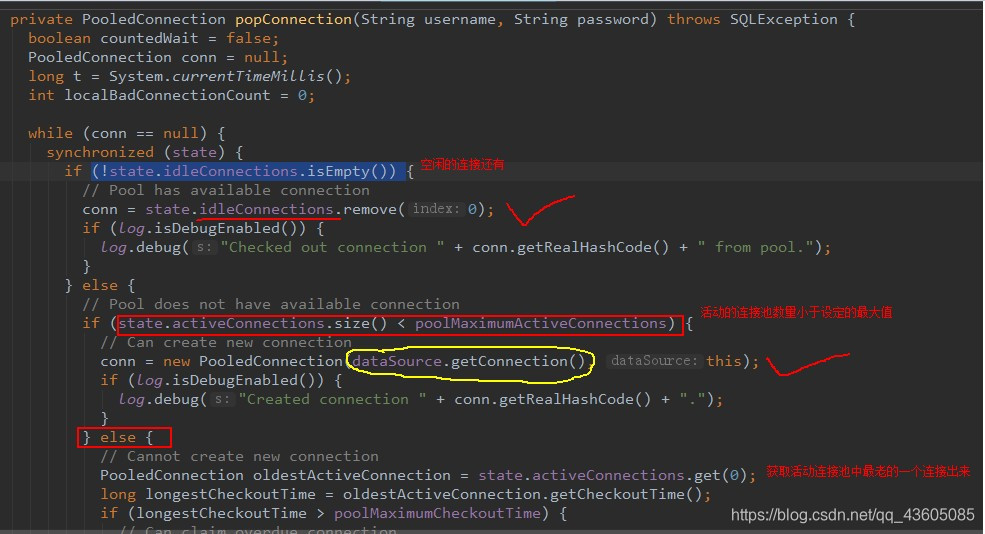
2.源码分析: (1)Mybatis 中 DataSource 的存取连接的获取 过程分析Connection对象
3.Mybatis的事务控制: JDBC 中事务可以通过手动方式将事务的提交改为手动方式,通过 setAutoCommit()方法 就可以开启事务 ,然后它是通过sqlsession对象的commit方法和rollback方法实现事务的提交和回滚
所以由于Mybatis底层也是使用Connection ,所以Mybatis事务 提交方法底层也是使用JDBC的setAutoCommit()方法和rollback() commit()
@After public void destory () throws Exception sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); in.close(); }
之前的 CUD 操作过程中,我们都要手动进行事务的提交 ,原因是 setAutoCommit()方法,在执行时它的值被设置为 false 了,所以我们在 CUD 操作中,必须通过 sqlSession.commit()方法来执行提交操作。
CUD 过程中必须使用 sqlSession.commit()提交事务?主要原因就是在连接池中取出的连接,都会将调connection.setAutoCommit(false)方法 ,这样我们就必须使用 sqlSession.commit()方法,相当于使用了 JDBC 中的 connection.commit()方法实现事务提交。明白这一点后,我们现在一起尝试不进行手动提交,一样实现 CUD 操作。
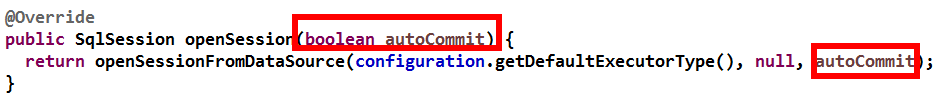
使用factory.openSession(true); 此时事务就设置为自动提交了,但是分析知道这种方法只能提交一份。
@Before public void init () throws Exception in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("SqlMapConfig.xml" ); SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(); SqlSessionFactory factory = builder.build(in); sqlSession = factory.openSession(true ); userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class ) ; } @After public void destory () throws Exception sqlSession.close(); in.close(); }
虽然这也是一种方式,但就编程而言,设置为自动提交方式为 false再根据情况决定是否进行提交 ,即这种方式更常用。
sqlSession = factory.openSession(); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); in.close();
二:Mybatis 的动态SQL语句 Mybatis 的映射文件中,前面我们的 SQL 都是比较简单的,有些时候业务逻辑复杂时,我们的 SQL 是动态变化 的,此时在前面的学习中我们的 SQL 就不能满足要求了。
(1)if 标签 标签的 test 属性中写的是对象的属性名(User里面的) ,如果是包装类的对象要使用 OGNL 表达式的写法。另外要注意 where 1=1 的作用~!
<select id="findUserByCondition" resultMap="userMap" parameterType="user" > select * from user where 1 = 1 <if test="userName != null" > and username = #{userName} </if> <if test="userSex != null" > and sex = #{userSex} </if> </select>
(2)where 标签 简化上面 where 1=1 的条件拼装 ,使得SQL语句看起来简单,我们可以采用标签来简化开发。
<select id="findUserByCondition" resultMap="userMap" parameterType="user" > select * from user <where> <if test="userName != null" > and username = #{userName} </if> <if test="userSex != null" > and sex = #{userSex} </if> </where> </select>
(3)foreach 标签 传入多个 id 查询用户信息 ,我们在进行范围查询 时,就要将一个集合中的值,作为参数动态添加进来。where id in (?) 它的属性:
foreach标签的属性: < foreach collection =”ids” open=”and id in (“ close=”)” item = “userId” separator=”,” >
collection:代表要遍历的集合 元素,注意编写时不要写#{}open:代表语句的开始部分 每个元素,生成的变量名
<!-- 根据queryvo中的Id集合实现查询用户列表--> <select id="findUserInIds" resultMap="userMap" parameterType="queryvo" > select * from user <where> <if test="ids != null and ids.size() > 0" > <foreach collection="ids" open="and id in (" close=")" item = "userId" separator="," > #{userId} </foreach> </if> </where> </select> </mapper>
三:Mybatis多表查询之 一对(一)多 1. 一对一查询: 方法一:(定义AccountUser来输出) (1)定义账户信息的实体类():Account :id,uid(对应用户的id),money
public class Account implements Serializable private Integer id; private Integer uid; private Double money;
(2)编写SQL语句:select account.,user.username, user.address * from account, user** where account.uid = user.id账号表中的信息和用户表中的用户名和地址 ,当账号对应的用户id与用户表中user对应)
(3)定义 AccountUser 类:为了能够封装上面 SQL 语句的查询结果(账号所有信息和用户的用户名和地址) ,定义 AccountUser 类中要包含账户信息同时还要包含用户信息,所以我们要在定义 AccountUser 类时可以继承 Account 类 。
public class AccountUser extends Account private String username; private String address;
(4)定义层账户的持久层Dao接口:
public interface IAccountDao List<Account> findAll () ; }
(5)定义 IAccountDao.xml 文件中的查询配置信息:
<select id="findAllAccout" resultType="accountuser" > select a.*,u.username,u.address from account a , user u where u.id = a.uid </select>
注意:因为上面查询的结果中包含了账户信息同时还包含了用户信息 ,所以我们的返回值类型 returnType
(6)创建 AccountTest 测试类执行即可。
总结:定义专门的 AccountUser 类作为输出类型 ,其中定义了 sql 查询结果集所有的字段。此方法较为简单,企业中使用普遍。
方法二:(resultType为Account来输出)以后最常用 账户实体类(Account)中包含用户
<!-- 定义封装account和user的resultMap--> <resultMap id="accountUserMap" type="account" > <id property="id" column="aid"></id> <result property="uid" column="uid"></result> <result property="money" column="money"></result> <!-- 一对一的关系映射:配置封装user的内容--> <association property="user" column="uid" javaType="user" > <id property="id" column="id"></id> <result property="username" column="username"></result> <result property="address" column="address"></result> <result property="sex" column="sex"></result> <result property="birthday" column="birthday"></result> </association> </resultMap>
(1)修改账号实体类(Account):
public class Account implements Serializable private Integer id; private Integer uid; private Double money; private User user;
(2)重新定义 IAccountDao.xml 文件 (重新写resultMap)
<!-- 定义封装account和user的resultMap--> <resultMap id="accountUserMap" type="account" > <id property="id" column="aid"></id> <result property="uid" column="uid"></result> <result property="money" column="money"></result> <!-- 它是用于指定从表方的引用实体属性的,配置封装user的内容--> <association property="user" javaType="user" > <id property="id" column="id"></id> <result property="username" column="username"></result> <result property="address" column="address"></result> <result property="sex" column="sex"></result> <result property="birthday" column="birthday"></result> </association> </resultMap>
2. 一对多查询:(resultMap) 用户信息和他的账户信息为一对多关系(用户多个账号的查询) ,并且查询过程中如果用户没有账户信息,此时也要将用户信息查询出来,我们想到了左外连接查询比较合适。,a.id as aid,a.uid,a.money * from account a, user u** where u.id = a.id;
(2)User类加入List< Account> (多个账号)
public class User implements Serializable private Integer id; private String username; private String address; private String sex; private Date Birthday; private List<Account> accounts;
(3) 用户持久层 Dao 映射文件配置(IUserDao.xml)
<resultMap type="user" id="userMap" > <id column="id" property="id"></id> <result column="username" property="username" /> <result column="address" property="address" /> <result column="sex" property="sex" /> <result column="birthday" property="birthday" /> <!-- collection 是用于建立一对多中集合属性的对应关系ofType 用于指定集合元素的数据类型--> <collection property="accounts" ofType="account" > <id column="aid" property="id" /> <result column="uid" property="uid" /> <result column="money" property="money" /> </collection> </resultMap> <!-- 配置查询所有操作 --> <select id="findAll" resultMap="userMap" > select account.*,user.username, user.address from account, user where account.uid = user.id </select>
(4)编写测试方法即可
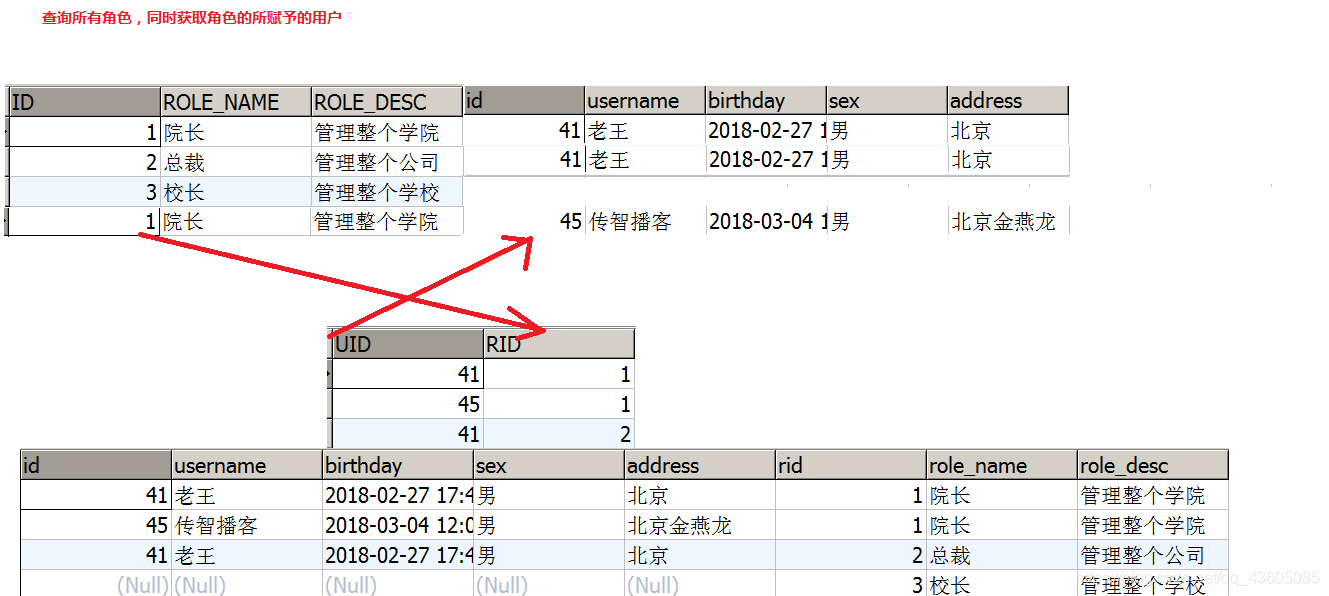
四:Mybatis多表查询之 多对多 1.实现 Role 到 User 多对多 用户与角色的关系模型: 一个角色可以赋予多个用户
select u.*,r.id as rid,r.role_name,r.role_desc from role r left outer join user_role ur on r.id = ur.rid left outer join user u on u.id = ur.uid
(2)编写角色实体类(Role):
public class Role implements Serializable private Integer roleId; private String roleName; private String roleDesc; private List<User> users;
(3)编写 Role 持久层映射配置文件(IRoleDao.xml):
<!--定义role表的ResultMap--> <resultMap id="roleMap" type="role" > <id property="roleId" column="rid"></id> <result property="roleName" column="role_name"></result> <result property="roleDesc" column="role_desc"></result> <collection property="users" ofType="user" > <id column="id" property="id"></id> <result column="username" property="username"></result> <result column="address" property="address"></result> <result column="sex" property="sex"></result> <result column="birthday" property="birthday"></result> </collection> </resultMap> <!--查询所有--> <select id="findAll" resultMap="roleMap" > select u.*,r.id as rid,r.role_name,r.role_desc from role r left outer join user_role ur on r.id = ur.rid left outer join user u on u.id = ur.uid </select>
(4)最后编写测试类
2.实现 User 到 Role 的多对多 一个用户可以具有多个角色,这样用户到角色的关系也还是一对多关系。这样我们就可以认为 User 与 Role 的多对多关系,可以被拆解成两个一对多关系来实现。
后面的SQL语句,角色实体类, 持久层映射配置文件同理。